CPU Affinity.
CPU affinity is the ability to bind process or thread to processor.
It is useful when you need to run a given process on a specific CPU/Core.
This can be very usefull specifically in two situations,
- When you need to reduce cache miss rate.
- When you are running real-time or time sensitive applications.
You can set the CPU affinity on linux using the tool
taskset.
If you want to set the CPU affinity programatically, it can be done using
sched_setaffinity.
For a thread CPU affinity can be set using
pthread_setaffinity_np
and pthread_attr_setaffinity_np
In this post I’ll be covering setting CPU affinity for pthreads.
How do we do that and how do we verify?
In order to set the affinity and verify that the given thread is running on the
specific CPU.
- Get a piece of code which is CPU intensive.
- Run it in two separate threadas.
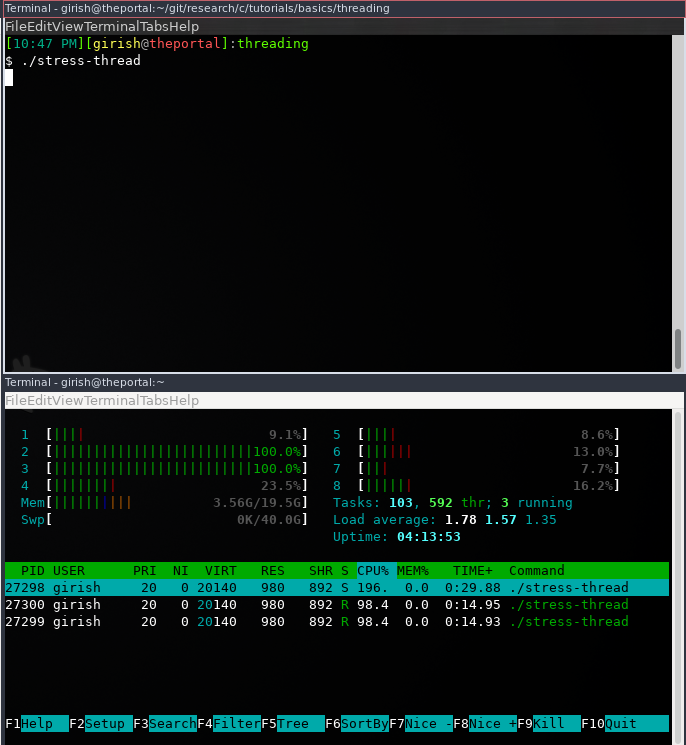
- Check in
htopif they switch the cores. - In the next step, get the number of available cores.
- Create a
CPUSETwith oneCPU. - Start the thread with affinity to that
CPUSET. - Observe in
htopif the threads switch cores.
The code.
The CPU intensive code.
We can calculate something in an infinite loop.
#include <math.h>
void *cpu_intensive_function(void *args){
float x = 1.5f;
while (1)
{
x *= sin(x) / atan(x) * tanh(x) * sqrt(x);
}
}Create threads
#include <pthread.h>
int main(){
pthread_t th1;
pthread_t th2;
int th1_op = pthread_create(&th1, NULL, cpu_intensive_function, NULL);
int th2_op = pthread_create(&th2, NULL, cpu_intensive_function, NULL);
pthread_join(th1, NULL);
pthread_join(th2, NULL);
return 0;
}When you run this code, you can observe in htop that the threads switch the
cores.
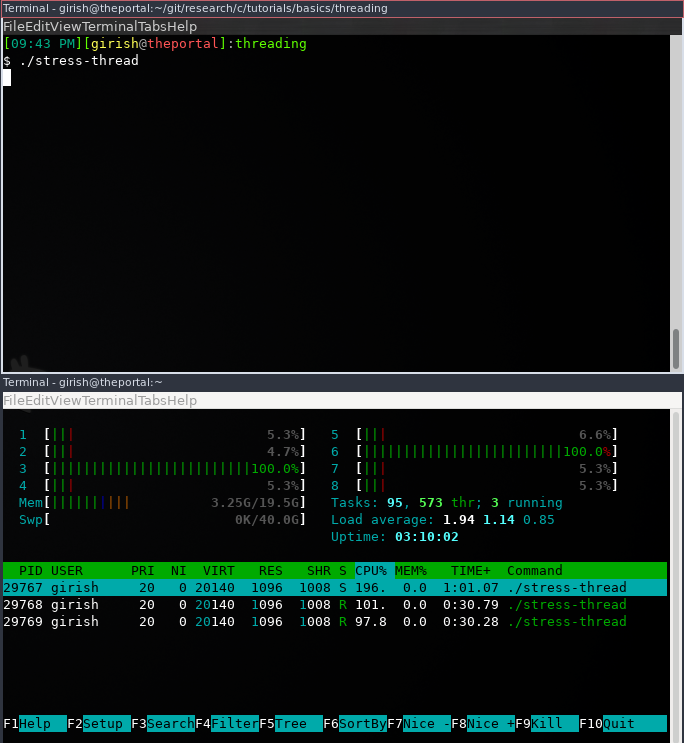
A few moments later.
Create CPUSETs.
cpu_set_t represents the set of CPUs that can be used for scheculing a
thread/process on that set of CPUs.
// Create a cpuset
cpu_set_t cpuset_1;
// Clear the cpuset
CPU_ZERO(&cpuset_1);
// add cpu core 1 to the cpuset
CPU_SET(1, &cpuset_1);Set the CPU affinity.
pthread_setaffinity_np() takes a thread, length of buffer pointed to
cpu_set_t, and a cpu_set_t as the arguments.
It basically sets the CPU affinity mask for the given thread to the given set
of CPUs.
#include <errno.h>
#define handle_error_en(en, msg)\
do { errno = en; perror(msg); exit(EXIT_FAILURE);} while (0);
// create a cpu set with core 1
cpu_set_t cpuset_1;
CPU_ZERO(&cpuset_1);
CPU_SET(1, &cpuset_1);
// create a cpu set with core 2
cpu_set_t cpuset_2;
CPU_ZERO(&cpuset_2);
CPU_SET(2, &cpuset_2);
pthread_t th1;
pthread_t th2;
int ret1;
int ret2;
/* initialize threads */
ret1 = pthread_create(&th1, NULL, cpu_intensive_function, NULL);
ret2 = pthread_create(&th2, NULL, cpu_intensive_function, NULL);
/* Set the affinity to thread 1*/
s1 = pthread_setaffinity_np(th1, sizeof(cpu_set_t), &cpuset_1);
if (s1 != 0)
handle_error_en(s1, "pthread_set_affinity_np, s1");
/*set the affinity to thread 2*/
s2 = pthread_setaffinity_np(th2, sizeof(cpu_set_t), &cpuset_2);
if (s2 != 0)
handle_error_en(s2, "pthread_set_affinity_np, s2");
// wait for the threads to terminate.
pthread_join(th1, NULL);
pthread_join(th2, NULL);Putting everything together.
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define handle_error_en(en, msg)\
do { errno = en; perror(msg); exit(EXIT_FAILURE);} while (0);
void *cpu_intensive_function(void *args){
float x = 1.5f;
while (1)
{
x *= sin(x) / atan(x) * tanh(x) * sqrt(x);
}
}
int main(){
// create a cpu set with core 1
cpu_set_t cpuset_1;
CPU_ZERO(&cpuset_1);
CPU_SET(1, &cpuset_1);
// create a cpu set with core 2
cpu_set_t cpuset_2;
CPU_ZERO(&cpuset_2);
CPU_SET(2, &cpuset_2);
pthread_t th1;
pthread_t th2;
int ret1;
int ret2;
/* initialize threads */
ret1 = pthread_create(&th1, NULL, cpu_intensive_function, NULL);
ret2 = pthread_create(&th2, NULL, cpu_intensive_function, NULL);
/* Set the affinity to thread 1*/
int s1 = pthread_setaffinity_np(th1, sizeof(cpu_set_t), &cpuset_1);
if (s1 != 0)
handle_error_en(s1, "pthread_set_affinity_np, s1");
/*set the affinity to thread 2*/
int s2 = pthread_setaffinity_np(th2, sizeof(cpu_set_t), &cpuset_2);
if (s2 != 0)
handle_error_en(s2, "pthread_set_affinity_np, s2");
// wait for the threads to terminate.
pthread_join(th1, NULL);
pthread_join(th2, NULL);
return 0;
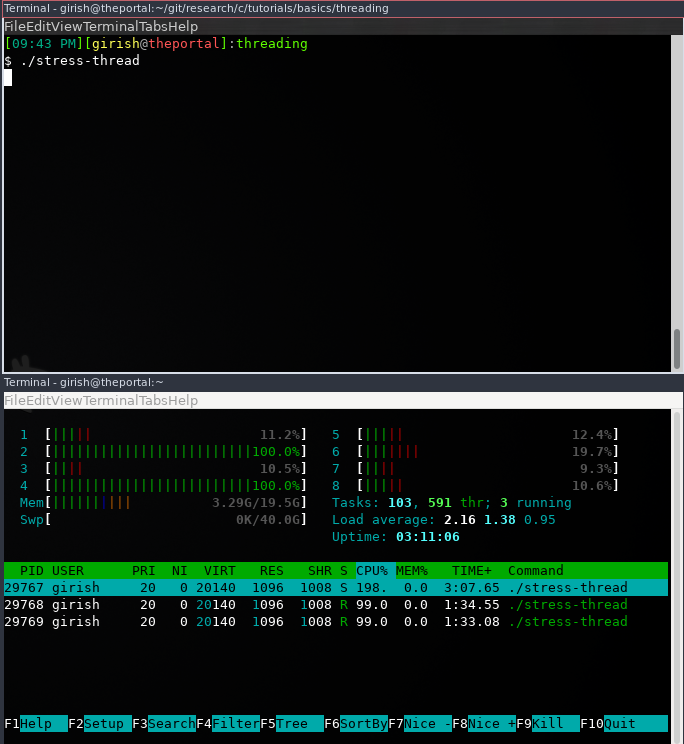
}When you observe in hopt, you will be able to see that now the threads are not switching the cores anymore.